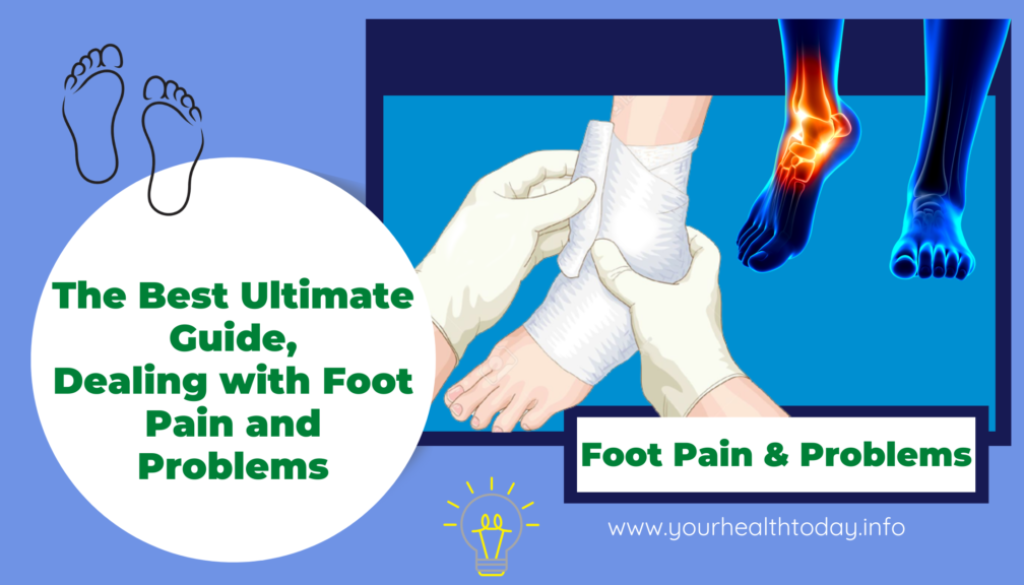
The Best Ultimate 2023 Guide on Foot Pain and Problems!
“Discover Expert Insights and Effective Solutions for Foot Pain in Our Comprehensive Guide. Learn about Problems, Causes, and Proven Remedies.”
Introduction
Foot Pain and Problems plague countless individuals, stemming from a myriad of causes such as injuries, medical conditions, or ill-fitting footwear.
These issues can dramatically diminish one’s quality of life, manifesting as discomfort, restricted mobility, or even more severe complications.
To safeguard overall well-being, it’s imperative to understand the root causes and explore potential solutions for Foot Problems.
Effectively managing these challenges is pivotal for promoting Foot Health and preventing further complications.
Ignoring Foot Pain can lead to chronic conditions, increased immobility, and a general decline in physical activity.
However, by recognizing the subtle signs of Foot Problems and taking proactive measures, individuals can not only alleviate pain but also stave off future injuries, thus enhancing their overall quality of life.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, offering in-depth insights and practical advice on understanding, addressing, and managing various Foot Problems.
It delves into an array of topics, including Common Causes of Foot Pain, Self-care Techniques, Essential Preventive Measures, and the right time to Seek Professional Help.
Additionally, it explores various Treatment Options, Lifestyle Adjustments, and Recommended Footwear tailored to support optimal Foot Health.
By the journey’s end, readers will possess a profound understanding of Foot Problems and the knowledge to take proactive steps, ensuring Healthy and Pain-free Feet for a vibrant life ahead.
Disclosure
Before delving further into the content, it’s essential to establish a foundation of clarity and transparency.
It’s worth noting that this post might be enriched with affiliate links, which serve as a means to sustain the quality of this platform.
These links come with a distinct advantage – they grant me a modest commission, a portion that comes directly from the seller and doesn’t include any additional costs on your end.
Intriguingly, some of these links also offer you a noteworthy benefit: exclusive discounts that are accessible through these very channels. It’s a win-win scenario.
By clicking and making purchases via these links, you extend your support toward the continuous upkeep and enhancement of this blog.
Your actions foster the creation of genuine, insightful content that’s dedicated to your enrichment.
It’s imperative to emphasize that I find genuine satisfaction in endorsing tools and resources that I hold dear, employ regularly, and have personally vetted.
This ensures that the content I present is not only reliable but also backed by firsthand experience.
As you immerse yourself in the post, my sincere hope is that it serves you in meaningful ways. May it contribute to your knowledge reservoir or introduce you to new insights.
Your commitment is genuinely appreciated.
Wishing you an enlightening reading experience ahead!
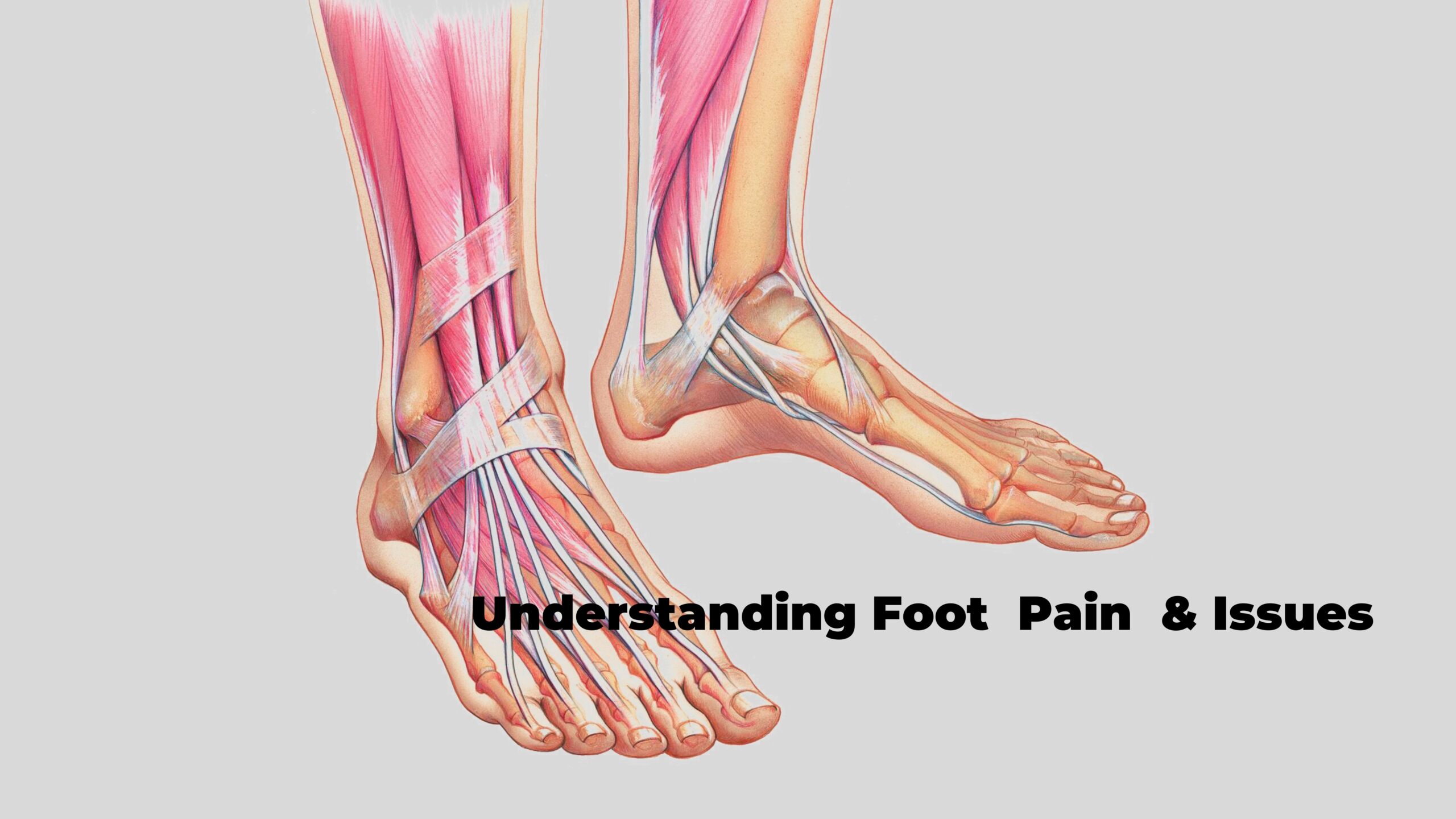
I – Understanding Foot Pain and Problems
Foot Pain and Issues cast a substantial shadow over our well-being, restricting mobility and inflicting discomfort in our daily lives.
In this section of the blog post, we lay the groundwork for understanding Foot Pain.
We define its various types, delve into common foot problems, unravel the causes behind the foot pain and problems, and shed light on the often-telling symptoms that accompany these issues.
This knowledge will equip the reader with the power to proactively address and enhance Foot Health, ensuring a more comfortable and mobile future.
A – Definition and Types of Foot Pain
Foot Pain encompasses a spectrum of discomfort, from mild aches to intense throbbing sensations, experienced within the feet.
Discerning the nuances among the various types of foot pain is vital for pinpointing underlying causes and tailoring precise treatments.
Let’s explore the issue below, as we outline some of the most prevalent forms of foot pain:
01 – Generalized Foot Pain
Generalized Foot Pain refers to a widespread discomfort affecting the entire foot, rather than being confined to a specific area.
This broad category encompasses sensations of soreness and discomfort that pervade the entire foot.
The origins of this type of pain are diverse, stemming from overuse, wearing improper footwear, underlying medical conditions such as Arthritis or Neuropathy, and injuries.
Manifesting as a dull ache, throbbing sensation, or an overall hindrance to regular activities, generalized foot pain can significantly impact one’s quality of life.
Effective management involves understanding the root causes, addressing underlying medical conditions, and adopting appropriate self-care measures.
It is important to comprehensively tackle these factors, so individuals can alleviate generalized foot pain and work toward restoring optimal Foot Health.
02 – Heel Pain
Heel Pain, a prevalent form of foot discomfort, specifically targets the heel area and is frequently linked to various conditions, most notably Plantar Fasciitis.
This condition, characterized by inflammation in the plantar fascia—a robust tissue band connecting the heel bone to the toes—causes pain primarily at the bottom of the heel, especially upon waking or after periods of rest.
Aside from plantar fasciitis, heel pain can stem from conditions like Achilles Tendinitis, involving inflammation of the Achilles tendon linking the calf muscles to the heel bone, and the latter to the heel spur bony protrusions.
The intensity of heel pain varies, impacting mobility and daily routines significantly.
Accurate diagnosis, crucial for effective treatment, involves a comprehensive evaluation, including physical examination, medical history analysis, and possibly imaging tests.
Treatment approaches encompass a range of strategies: rest, targeted stretching exercises, orthotic devices, supportive footwear, physical therapy, and, in certain cases, medications or medical interventions.
Managing heel pain effectively is paramount. It not only alleviates discomfort but also fosters healing and curtails the risk of complications.
Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or Podiatrists ensures precise diagnosis and tailored treatment plans, addressing individual needs comprehensively.
03 – Arch Pain
Arch Pain, localized discomfort in the curved area between the ball of the foot and the heel, can stem from various factors like Plantar Fasciitis, Flat Feet (fallen arches), overuse, tarsal tunnel syndrome, inadequate footwear, or improper support.
Effectively managing arch pain requires a multi-faceted approach. This encompasses essential self-care measures and, when necessary, medical interventions.
Techniques including rest, ice therapy, targeted stretching exercises, wearing supportive shoes or orthotic inserts, and utilizing over-the-counter pain relievers are advisable.
In more persistent cases, healthcare professionals might recommend tailored approaches such as physical therapy or custom orthotics to alleviate discomfort.
For cases of enduring or severe arch pain, seeking prompt medical attention from a qualified healthcare professional or podiatrist is the wisest solution.
Their expertise can pinpoint the underlying causes, and they will guide toward appropriate treatments, ensuring a swift return to comfort and mobility.
04 – Toe Pain
Toe Pain, characterized by discomfort in one or multiple toes, can result from a variety of causes including ingrown toenails, bunions, hammertoe, mallet toe, gout, toe fractures, and neuropathy.
The approach to treating toe pain hinges upon its underlying cause. Self-care measures are often a first line of defense.
It can include maintaining proper foot hygiene, soaking the feet, opting for comfortable and well-fitting shoes, using toe splints or pads, and utilizing over-the-counter pain medications.
In instances where self-care proves insufficient, medical interventions may be necessary.
These could involve procedures such as ingrown toenail removal or bunionectomy, as well as addressing underlying medical conditions contributing to the pain.
Persistent, worsening, or pain accompanied by concerning symptoms warrants professional attention.
Consulting a healthcare professional or a podiatrist ensures an accurate diagnosis and opens avenues to appropriate and effective treatment options, tailored to the individual’s specific condition.
B – Common Foot Problems
Foot Health is a vital component of overall well-being often underestimated. Our feet, an intricate structure of bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, diligently support our daily activities.
However, this complexity makes them susceptible to various problems and conditions.
In this section of our comprehensive guide, we are going to shed light on Common Foot Problems, ranging from minor inconveniences like corn and calluses to more debilitating conditions such as plantar fasciitis and bunions.
Our exploration includes in-depth discussions on Causes, Symptoms, and Potential Treatment Options for these issues.
Our mission is to empower individuals with knowledge, enabling them to understand these Foot Conditions, identify early signs, and take proactive measures, including seeking professional medical assistance when need be.
The feet, bearing the weight of our entire body, provide stability and mobility. Neglecting Foot Health can profoundly impact overall well-being.
Prioritizing foot care and staying informed about potential problems constitute investments in long-term health.
Join the journey to explore and understand Common Foot Problems, ensuring our feet remain strong, pain-free, and capable of supporting us every step of the way.
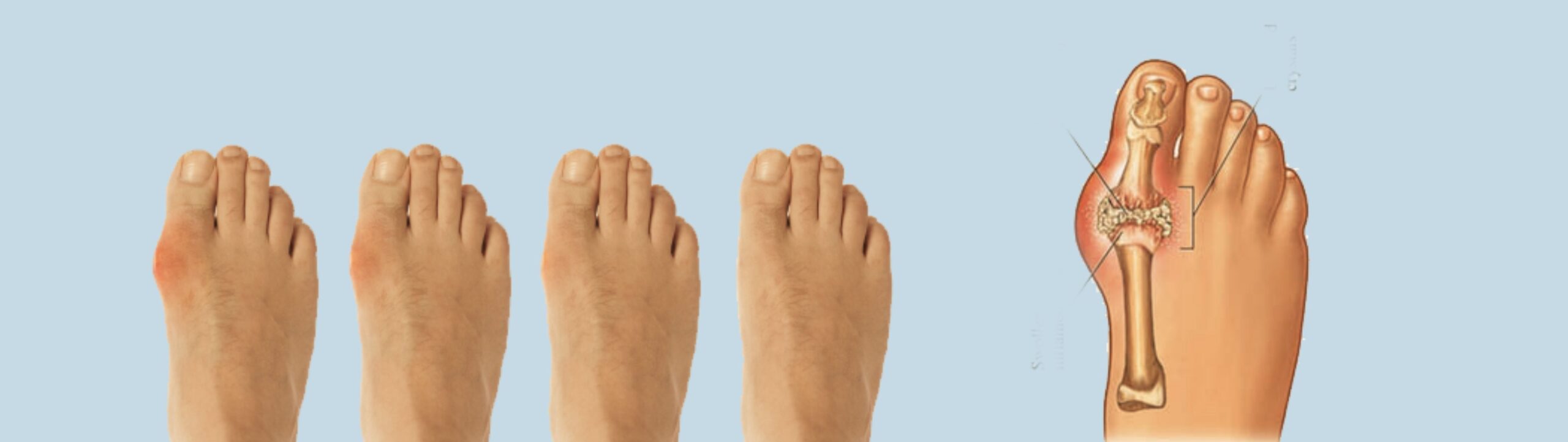
01 – Bunions
Bunions, a prevalent and frequently painful foot condition, manifest as a bony bump at the base of the big toe, causing it to angle towards the other toes.
This misalignment often results in discomfort, inflammation, and challenges in finding suitable footwear.
Developing gradually, bunions can be influenced by genetics, ill-fitting shoes, and specific foot conditions.
It predominantly affects women, because of their exacerbated will of wearing tight or narrow footwear, which further contributes to its progression and discomfort.

02 – Bromodosis (or Smelly Feet)
Bromodosis, commonly known as Smelly Feet, is a widespread and sometimes embarrassing condition marked by a foul odor emanating from the feet.
This issue can affect individuals of all ages, regardless of their lifestyle or hygiene practices.
The primary cause of foot odor is the perspiration produced by your feet. Unlike sweat from other body parts, foot sweat often cannot evaporate easily because it becomes trapped within socks and shoes.
This creates a warm and damp environment conducive to the growth of bacteria and fungi (fungus).
These microorganisms thrive on sweat and dead skin cells, releasing odorous substances as they multiply, resulting in the unpleasant smell associated with smelly feet.
Several factors contribute to this condition, including inadequate personal hygiene, wearing the same shoes daily, hormonal changes (especially during puberty and pregnancy), specific medications, and health conditions like hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating) or athlete’s foot.
03 – Calluses
Calluses, similar to corns, are thickened and hardened patches of skin that commonly form on the soles of the feet or areas subjected to repeated friction or pressure.
They often result from activities involving repetitive motion or pressure, like walking or running, and can be worsened by wearing ill-fitting shoes.
These calluses present as yellowish, toughened patches of skin, feeling rough or hardened when touched.
While they are typically not painful, they can occasionally become sensitive or uncomfortable, especially if they grow excessively thick.
04 – Corns
Corns, a prevalent foot problem, can indeed cause discomfort and pain. These thickened and hardened patches of skin usually form on the toes or the soles of the feet.
They commonly result from friction or pressure caused by ill-fitting shoes, repetitive activities, or abnormal foot anatomy.
05 – Flat Feet or Fallen Arches
Flat Feet, also referred to as Fallen Arches, are common foot conditions characterized by lower or flattened arches, causing the entire sole to make contact with the ground.
This condition can strain the ligaments and muscles supporting the arch, resulting in discomfort and various symptoms including foot fatigue, and an elevated risk of developing other foot pain and problems.
Flat feet can be congenital, present at birth, or acquired due to factors such as age, injury, obesity, or repetitive stress on the feet.
This condition is often associated with overpronation, wherein the foot excessively rolls inward during walking or running, exacerbating the condition and increasing the risk of related discomfort and issues.
06 – Hammertoe and Mallet Toe
Hammertoe and Mallet Toe are foot deformities primarily affecting the second, third, or fourth toes.
In both conditions, a toe exhibits an abnormal bend in the middle joint, causing it to bend downward, resembling a hammer.
In hammertoe, which often affects the second toe, the proximal joint near the base buckles, shaping the toe with a hammer-like appearance.
In mallet toe, it’s the distal joint, furthest from the base, that bends upward from the ball of the foot and downward at the middle joint, creating a mallet-like shape.
These conditions are frequently caused by wearing tight or high-heeled shoes, which force the toes against the front of the shoe.
Muscle imbalances or certain diseases such as arthritis or diabetes can also contribute to their development
07 – Ingrown Toenails
An Ingrown Toenail, a prevalent condition primarily affecting the big toe, occurs when the corner or side of a toenail grows into the soft flesh of the toe, causing pain, redness, swelling, and potential infection.
Improper toenail trimming, specifically cutting them too short or not straight across, is the leading cause.
Additionally, wearing tight or narrow shoes that crowd the toes can contribute to ingrown toenails.
Some individuals naturally have toenails that curve and dig into the skin, while injuries to the toe can also result in this condition.
Early symptoms encompass pain and tenderness along one or both sides of the toenail, often exacerbated by wearing shoes.
The surrounding skin may become red and swollen, indicating the presence of an ingrown toenail.
08 – Onychomycosis (or Fungal Nail Infection)
Onychomycosis, commonly known as Fungal Nail Infections, is a prevalent condition that affects toenails or fingernails.
It leads to nail discoloration, thickening, and increased susceptibility to cracking and breaking. Although not typically serious, it can be both unsightly and uncomfortable.
Fungal nail infections are primarily caused by different types of fungi, with dermatophytes being the most common, while yeasts and molds also contribute in certain cases.
These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, transforming places like public swimming pools, showers, and locker rooms conducive to contracting a fungal nail infection.
Early symptoms often include a small white or yellow spot under the tip of the toenail or fingernail.
As the infection progresses, symptoms may escalate to thickened nails, distorted nail shape, brittleness, crumbliness, ragged nails, separation of nails from the underlying skin, dark discoloration due to debris accumulation under the nail, and a foul odor emanating from the infected nail.
09 – Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar Fasciitis is a prevalent and often incapacitating foot condition marked by the inflammation of the plantar fascia.
The plantar fascia is the thick tissue band running along the underside of the foot, connecting the heel bone to the toes.
This condition manifests as persistent heel pain, notably experienced during the initial steps in the morning or after periods of rest.
Plantar fasciitis typically arises from factors like overuse, repetitive strain, or abnormal foot mechanics, which place excessive stress on the plantar fascia.
Contributing factors include conditions such as flat feet or high arches, as well as tight calf muscles, obesity, and inadequate footwear.
These elements collectively contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis, making it a common and challenging foot ailment.
10 – Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition affecting the tibial nerve as it passes through a narrow passage known as the tarsal tunnel, situated on the inner side of the ankle.
Comparable to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in the wrist, this syndrome involves compression or pinching of the tibial nerve, resulting in pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness in the foot.
The tarsal tunnel is composed of bones, ligaments, and soft tissues that encase the tibial nerve.
Various factors can contribute to the development of tarsal tunnel syndrome.
These include anatomical variations, flat feet, ankle injuries, swelling, and systemic conditions like diabetes or arthritis.
A distinctive symptom associated with this condition is the sensation of electric shocks radiating along the inner side of the ankle and into the foot.
11 – Toe Fractures
A Toe Fracture, commonly known as a broken toe, happens when one or more of the toe bones (phalanges) are fractured.
This injury can occur due to various incidents, such as heavy objects falling on the foot or forcefully stubbing the toe against a wall or furniture.
Typical symptoms of a toe fracture encompass pain, swelling, bruising, stiffness, and challenges in walking or wearing shoes.
In severe cases, the fracture can lead to a visible deformity, causing the toe to appear crooked or abnormal.
C – Causes of Foot Pain and Problems
Foot Pain and Problems can arise from various sources, often linked to lifestyle choices or underlying health conditions.
Issues such as ill-fitting footwear, overuse, and injuries can cause discomfort and worsen foot problems.
Conditions like plantar fasciitis, bunions, hammertoe, and mallet toe are often a result of poor footwear choices or high-impact activities, leading to inflammation, deformities, and pain.
Common problems like ingrown toenails occur due to improper toenail trimming or tight shoes, causing the nail to grow into the surrounding skin, leading to pain and potential infections.
Additionally, systemic diseases significantly contribute to foot problems.
Arthritis, including Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Gout, can cause joint inflammation and degeneration, leading to foot pain.
Diabetes, a prevalent systemic condition, can cause peripheral neuropathy and impaired circulation, resulting in numbness, tingling, and an increased risk of foot ulcers and infections.
Morton’s Neuroma, a painful condition involving nerve tissue thickening, often leads to sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot.
Regardless of the cause, persistent or severe foot pain warrants professional medical evaluation for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
D – Associated Symptoms with Foot Pain and Problems
Foot Pain and Problems can present with a diverse range of symptoms, varying from mild discomfort to severe pain, impacting mobility and overall quality of life significantly.
The most common symptom is pain in one or multiple parts of the foot, which can occur suddenly, as in the case of injuries or sprains, or a gradually developed pain due to conditions like plantar fasciitis or bunions.
Pain can manifest in different forms, such as sharp, stabbing sensations, dull aches, or burning feelings. It may be localized to specific areas like the heel, arch, ball of the foot, and toes, or encompass the entire foot.
Added to this pain, can foot problems often be accompanied by other symptoms. Swelling or inflammation can indicate injuries or underlying conditions like arthritis or gout.
Changes in the skin or nails due to conditions such as corns, calluses, blisters, ulcers, or fungal infections, are common indicators of foot issues.
Alterations in foot color or temperature, as well as sensations of numbness and tingling, may suggest issues related to circulation or nerve function.
Furthermore, changes in foot shape or structure, like flat feet or high arches, and difficulties in movement, such as limping or hesitancy to put weight on the foot, can signal various foot conditions.
It’s crucial to recognize that these symptoms can signify a wide array of issues, ranging from minor ailments to potentially serious medical conditions, underscoring the importance of professional evaluation and care.
II – Impact of Foot Pain and Problems on Overall Health
Foot Pain and Problems exert a significant influence on an individual’s overall health and well-being, extending far beyond immediate discomfort.
These issues can trigger a chain of consequences that affect mobility, disrupt daily activities, and even impact mental health.
When left unexpectedly, foot problems can contribute to enduring health complications, including musculoskeletal disorders, joint degeneration, and an elevated risk of falls.
Recognizing the comprehensive impact of foot pain is pivotal in understanding the importance of early intervention and preventive measures.
This section delves into the multifaceted effects of foot pain on daily life, long-term health, and psychological well-being, underscoring the crucial need to address and manage foot pain and problems.
By doing so, individuals can uphold their Optimal Overall Health and quality of life.
A – Effects on Daily Life
Foot Pain and Problems can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life. The discomfort and limitations caused by these issues can hinder mobility and affect various aspects of a person’s routine.
Following are some key points highlighting these effects:
01 – Mobility and Independence
Foot pain and issues can make it difficult for individuals to walk, stand, or engage in physical activities, thereby compromising their mobility and independence.
Simple tasks such as walking to the grocery store, climbing stairs, or participating in recreational activities may become challenging or even impossible.
02 – Working and Productivity
For individuals whose occupations require being on their feet or involve physically demanding tasks, foot pain can directly affect their ability to perform their job effectively.
Standing or walking for prolonged periods may become unbearable, leading to increased unproductivity and potentially affecting their professional growth and income.
03 – Hygiene and Personal Care
Foot pain and problems can also impede personal care activities such as bathing, grooming, and even wearing certain types of footwear.
The discomfort may limit a person’s ability to properly clean and care for their feet, which can increase the risk of developing further complications like infections or skin conditions.
04 – Social Engagement and Recreational Activities
Foot problems can limit a person’s social life and participation in recreational activities.
They may have to decline invitations to social events, gatherings, or outings that involve prolonged periods of standing or walking.
This restriction can lead to feelings of isolation, reduced quality of life, and potential psychological effects.
B – Long-Term Impacts on Overall Health
Foot pain and problems can have significant long-term impacts on a person’s Overall Health and well-being.
Ignoring or neglecting foot issues can lead to various complications and affect multiple body systems.
Next are some important considerations regarding the long-term effects:
01 – Altered Gait and Posture
Chronic foot pain can alter a person’s gait (the way they walk) and posture.
Compensation for the discomfort may cause changes in the alignment of the feet, ankles, knees, hips, and spine, leading to further musculoskeletal issues, such as joint pain, back pain, and an increased risk of injuries.
02 – Gasket Degeneration
Certain foot conditions, such as Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis, can cause joint degeneration over time.
The ongoing inflammation and stress on the joints due to foot pain can accelerate the breakdown of cartilage and contribute to the development of chronic joint problems, affecting mobility and overall joint health.
03 – Unbalance and Fall Risks
Foot pain and problems can disrupt the body’s balance and stability, increasing the risk of falls and related injuries, especially among older adults.
A compromised ability to maintain proper balance may lead to fractures, sprains, and other injuries that can have serious consequences on an individual’s health and independence.
04 – Systemic Health Condition
Foot conditions can also be associated with Systemic Health Conditions.
For example, uncontrolled diabetes can lead to nerve damage in the feet (diabetic neuropathy) and poor circulation, increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
Additionally, foot pain can indirectly impact other aspects of health, such as sleep disturbances, weight gain due to reduced physical activity, and overall diminished quality of life.
C – Psychological Implications
Foot pain and problems can have significant psychological implications, affecting a person’s mental and emotional well-being.
Below are some psychological aspects influenced by foot pain and issues:
01 – Emotional Distress
Chronic foot pain can lead to emotional distress, including feelings of frustration, irritability, and sadness.
The constant discomfort and limitations imposed by foot problems may create a sense of helplessness, impacting one’s overall mood and emotional state.
02 – Reduced Quality of Life
Foot issues can diminish a person’s quality of life by limiting their ability to engage in activities they enjoy.
Hobbies, sports, and recreational pursuits may become challenging or impossible, leading to a sense of frustration, loss of interest, and decreased overall life satisfaction.
03 – Social Withdrawal and Isolation
Foot pain or problems can also contribute to social withdrawal and isolation.
The discomfort and limitations may make individuals hesitant to participate in social gatherings, events, or outings that involve standing or walking.
This isolation can lead to feelings of loneliness, social disconnection, and a negative impact on mental health.
04 – Anxiety and Depression
Living with chronic foot pain can increase the risk of developing anxiety and depression.
The persistent physical discomfort, along with the challenges it poses to daily life and activities, can create a constant source of stress and emotional strain.
Over time, this can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health conditions.
05 – Body Image and Self-Esteem
Foot problems, especially those that affect the appearance or functionality of the feet, can impact body image and self-esteem.
Individuals may feel self-conscious about their feet, avoid wearing certain types of footwear, or experience a sense of embarrassment or shame. This can affect their overall self-confidence and self-perception.
06 – Sleep Disturbances
Foot pain and issues can also disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to sleep disturbances.
The discomfort may make it difficult to find a comfortable sleeping position or result in nighttime awakenings, leading to poor sleep quality and subsequent daytime fatigue and irritability.
Conclusion
It is important to recognize the comprehensive impact of foot pain and problems on daily life, long-term health, and psychological well-being.
Seeking timely medical attention and implementing appropriate interventions, such as proper foot care, orthotics, physical therapy, and pain management strategies, can help alleviate the effects and improve overall functioning and quality of life.
III – Preventive Measures for Foot Problems
Prioritizing preventive measures to maintain Foot Health is crucial for overall well-being and mobility. Foot problems can substantially affect daily life, overall health, and psychological well-being.
By adopting straightforward practices, individuals can minimize the risk of developing foot issues and safeguard the long-term health of their feet.
This section will outline essential preventive measures, emphasizing proper foot care, the importance of suitable footwear, and the role of diet and exercise in promoting foot health.
Understanding and integrating these measures enable individuals to proactively protect their feet, ensuring a life free from the limitations and discomfort associated with foot problems.
A – Proper Foot Care
Proper foot care is essential for maintaining the health and well-being of the feet.
By incorporating regular foot care practices into one’s routine, individuals can reduce the risk of developing foot issues. Following are some key aspects of proper foot care:
01 – Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Regularly washing and drying the feet helps to keep them clean and free from bacteria or fungi that can cause infections.
Inspecting the feet for any signs of abnormalities such as cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling can also help identify potential issues early on.
02 – Moisturizing
Keeping the skin of the feet moisturized helps prevent dryness, cracks, and fissures.
Applying a moisturizing cream or lotion to the feet, especially after bathing, can help maintain the skin’s hydration and suppleness.
03 – Proper Nails Trimming
It is important to trim toenails straight across and avoid cutting them too short or rounding the edges. This reduces the risk of ingrown toenails and potential infections.
04 – Avoiding Harsh Chemicals
Harsh chemicals, such as strong soaps or aggressive foot treatments, can damage the skin and increase the risk of skin irritation or infections.
It is recommended to use mild, gentle products when caring for the feet.
B – Importance of Suitable Footwear
Wearing appropriate footwear is crucial for preventing foot problems and ensuring proper foot support and comfort.
Ill-fitting or unsuitable shoes can contribute to various foot conditions. Consider the following points when selecting footwear:
01 – Proper Fit
Shoes should fit well and provide adequate room for the toes to move freely. Shoes that are too tight or too loose can cause friction, pressure points, and discomfort.
02 – Arch Support
Shoes with proper arch support help maintain the natural arches of the feet, promoting better alignment and reducing the risk of conditions like flat feet or plantar fasciitis.
Arch support can be achieved through built-in arches, orthotic inserts, or customized insoles.
03 – Cushioning and Shock Absorption
Shoes with adequate cushioning and shock absorption properties help reduce the impact on the feet when walking or engaging in physical activities.
This is particularly important for individuals with conditions such as arthritis or heel pain.
04 – Breathable Materials
Choosing shoes made from breathable materials, such as leather or mesh, allows air circulation, reducing the risk of excessive moisture and fungal infections.
05 – Appropriate Footwear for Specific Activities
Different activities require specific footwear. For instance, athletic activities may require supportive sneakers, while work boots protect the feet for heavy-duty tasks.
Selecting footwear suitable for the intended activity helps minimize the risk of foot injuries and discomfort.
C – Role of Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise can positively impact foot health and overall well-being.
Here are ways in which diet and exercise contribute to foot health:
01 – Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise helps reduce the load on the feet and lower limbs.
Excess weight can strain the feet and contribute to foot pain and conditions like plantar fasciitis or osteoarthritis.
02 – Strengthening and Flexibility
Engaging in exercises that specifically target the feet, ankles, and lower limbs can help strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility.
Exercises like toe curls, calf stretches, and ankle rotations can promote better foot function and reduce the risk of injuries.
03 – Traffic Promotion
Regular physical activity promotes proper blood circulation, which is vital for overall foot health.
Improved circulation helps deliver nutrients and oxygen to the feet, aiding in tissue repair and reducing the risk of peripheral vascular diseases.
04 – Nutrient-Rich Diet
Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals supports overall foot health.
Adequate intake of nutrients like Calcium, Vitamin D, and Omega-3 Fatty Acids can contribute to strong bones, healthy joints, and optimal tissue repair.
05 – Hydration
Maintaining proper hydration is important for foot health as well. Sufficient water intake helps keep the skin hydrated and reduces the risk of dryness and cracking.
06 – Disease Prevention
A healthy diet and regular exercise can contribute to the prevention of systemic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
These conditions can have detrimental effects on foot health and increase the risk of foot condition complications.
Conclusion
By incorporating these preventive measures into one’s lifestyle, individuals can proactively maintain Foot Health, reduce the risk of foot problems, and promote overall well-being.
It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and recommendations based on individual Foot Health needs.
IV – Professional Diagnosis and Treatment of Foot Pain and Problems
This segment of our comprehensive guide on Foot Pain and Problems is tailored to offer personalized care and effective solutions aimed at alleviating foot disorders and enhancing overall well-being.
Whether you’re looking for relief from common foot ailments like plantar fasciitis or bunions, or you need advanced treatments for more complex conditions, I encourage you to explore the Professional Diagnosis and Treatment of Foot Pain and Problems section next.
A – When to See a Doctor?
When experiencing foot issues, it’s important to understand when it’s necessary to seek medical attention from a doctor.
While some foot problems can be self-treated or managed with over-the-counter remedies, certain signs, and symptoms warrant professional evaluation.
Here are some indicators that it may be time to schedule an appointment with a doctor specializing in foot health:
01 – Persistent Pain
If you’re experiencing persistent or worsening pain in your feet that doesn’t subside with rest, or rather elevate itself, or the pain doesn’t seem to calm down using over-the-counter pain relievers, it’s essential to consult a doctor.
This could indicate an underlying condition or injury that requires medical intervention.
02 – Limited Mobility
Difficulty walking, standing, or engaging in normal activities due to foot pain or restricted movement is a red flag.
Seeking medical attention can help identify the root cause of the problem and provide appropriate treatment to restore mobility.
03 – Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling, redness, and inflammation in the feet can be indicative of various issues, such as an infection, gout, arthritis, or a stress fracture.
A doctor can perform a thorough examination, order diagnostic tests if necessary, and recommend suitable treatment options.
04 – Foot Deformities
If you notice any changes in the structure or appearance of your feet, such as a bunion, hammertoe, or other deformities, it’s advisable to consult a doctor.
These conditions can worsen over time and may require corrective measures to prevent further complications.
05 – Signs of Infection
If you notice any signs of infection, such as increased pain, warmth, redness, or discharge from a wound or cut on your foot, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Infections left untreated can lead to serious complications and of course a negative impact on your daily life.
06 – Numbness or Tingling
Persistent numbness, tingling sensations, or a “pins and needles” feeling in the feet could be an indication of nerve damage or a neurological condition.
A doctor can evaluate your symptoms, perform tests, and recommend appropriate treatment or referrals to a specialist.
07 – Diabetic Foot Complications
Individuals with diabetes should be particularly vigilant about Foot Care.
If you have diabetes and notice any foot issues, such as slow-healing wounds, ulcers, or changes in skin color or temperature, it’s important to consult a doctor promptly.
Diabetic foot complications can escalate rapidly and may require specialized care.
Conclusion
Remember, this list is not exhaustive, and any concern or uncertainty about your Foot Health should prompt you to reach out to a medical professional.
Timely intervention can help prevent further damage, alleviate pain, and improve your overall quality of life.
B – Foot Pain and Problems Diagnosis Process
The Diagnosis Process for Foot Pain and Problems involves a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional specializing in Foot Health.
Here’s an overview of what you can expect during the diagnostic process:
01 – Medical History
The first step in diagnosing foot pain or issues is discussing your medical history with the doctor.
They will inquire about any previous foot injuries, surgeries, underlying medical conditions, and medications you may be taking.
This information helps provide important context for your current symptoms.
02 – Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination of your feet will be conducted.
The doctor will visually inspect your feet, looking for any visible abnormalities, such as swelling, deformities, or skin changes.
They may also assess your posture and gait to evaluate how your feet function during movement.
03 – Palpation and Range of Motion
The doctor will use their hands to palpate the affected area, feeling for any tenderness, lumps, or abnormalities.
They may also check the range of motion in your foot and ankle joints to identify any limitations or issues.
04 – Diagnosis Tests
Depending on your specific symptoms and the initial examination, the doctor may recommend additional diagnostic tests to gather more information.
These tests can include X-rays, MRIs, CT Scans, Ultrasounds, or Bone Scans.
These imaging techniques can help identify fractures, arthritis, ligament injuries, or other structural abnormalities.
05 – Laboratory Tests
In certain cases, the doctor may order laboratory tests, such as blood work, to check for indicators of systemic conditions like gout or rheumatoid arthritis.
If there are signs of infection, they may also collect samples for culture and sensitivity testing.
06 – Specialized Examination
If necessary, the doctor may refer you to a Specialist for further evaluation.
For example, a Podiatrist may perform a Biomechanical Examination to assess your foot and ankle function during walking or recommend a nerve conduction study if nerve damage is suspected.
07 – Patient Feedback
Throughout the diagnostic process, it’s important to communicate openly with the doctor about your symptoms, pain levels, and any changes you’ve noticed.
Your feedback plays a crucial role in guiding the diagnosis and ensuring the most accurate assessment of your condition.
Once the doctor has gathered all the necessary information, they will provide you with a diagnosis based on their findings.
They will explain the nature of your foot condition, discuss the underlying causes, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Treatment may involve a combination of conservative measures, such as rest, physical therapy, orthotics, medication, or in some cases, surgical intervention.
To notice is, the diagnosis process may vary depending on the specific symptoms and circumstances.
It’s important to consult a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
C – Common Treatments for Foot Problems
Foot Problems, as discussed earlier, can cause significant discomfort and impede our daily activities.
Whether it’s aching arches, ingrown toenails, plantar fasciitis, or other conditions, seeking appropriate treatment is essential for maintaining optimal Foot Health.
Fortunately, there are various common treatments available to address various foot problems and alleviate pain and discomfort.
In this section, we will explore some of the most frequently utilized treatments for foot issues.
We will delve into Medication, Physical Therapy, Surgery, and Alternative Therapies, covering a range of approaches that can enhance foot conditions and restore mobility.
We emphasize that while these treatments can provide relief for many individuals, consulting with a healthcare professional or Podiatrist is always advisable to receive an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Whether you’re dealing with a minor issue or a chronic condition, understanding the available treatment options empowers you to make informed decisions about your Foot Health.
Let’s delve into these Common Treatments for Foot Problems, enabling us to take proactive steps towards healthier and happier feet.
01 – Medication
Medications are often used to manage foot pain and reduce inflammation associated with various foot conditions.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) like Ibuprofen or Naproxen Sodium are commonly prescribed to alleviate pain and swelling.
Topical Creams or Ointments containing analgesics or anti-inflammatory agents may also be recommended to provide localized relief.
In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered directly into the affected area to provide more targeted and potent anti-inflammatory effects.
02 – Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in foot problem treatment by improving strength, flexibility, and overall foot function.
A physical therapist may employ various techniques such as stretching exercises, range-of-motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and manual therapy to alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and promote proper foot mechanics.
They may also recommend the use of Orthotic Devices, such as shoe inserts or custom-made orthotics, to support and align the foot properly.
03 – Surgery
When conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, or in cases of severe foot deformities or injuries, surgery may be considered.
Foot surgery aims to correct structural abnormalities, repair damaged tissues, and restore proper function.
Procedures can range from minor interventions, such as bunionectomy or hammertoe correction, to more complex surgeries like joint fusions, tendon repairs, or even ankle or foot reconstruction.
Surgical approaches vary depending on the specific condition and the individual’s unique needs.
04 – Alternative Therapies
Some individuals seek alternative or complementary therapies to complement traditional treatments for foot problems.
These therapies include options such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, massage therapy, and herbal remedies.
While evidence regarding the effectiveness of Alternative Therapies for foot problems is often anecdotal, some individuals report subjective improvements in pain management and overall well-being.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before pursuing Alternative Therapies to ensure their safety and compatibility with the primary treatment plan.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that the choice of treatment depends on the specific foot condition, its severity, and individual factors.
A healthcare professional specializing in Foot Health will assess your condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment option tailored to your needs.
It’s crucial to follow their guidance and actively participate in the prescribed treatment plan to achieve the best possible outcomes for your Foot Health.
D – The Role of a Podiatrist
A Podiatrist, also known as a Podiatric Physician or Foot Doctor, is a specialized healthcare professional dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of foot and ankle disorders.
Through rigorous education and training, Podiatrists acquire expertise in addressing a wide array of foot-related conditions, offering comprehensive foot care services.
Let’s explore the role of a Podiatrist in greater detail:
01 – Diagnosis
One of the primary responsibilities of a Podiatrist is to accurately diagnose foot and ankle conditions.
They utilize their expertise in examining the lower extremities, analyzing symptoms, and conducting diagnostic tests such as X-rays, Ultrasounds, or Laboratory Tests.
Podiatrists are skilled in identifying various foot problems, including fractures, sprains, infections, structural abnormalities, nerve damage, skin conditions, and more.
02 – Treatment
Podiatrists employ various treatment modalities to address foot and ankle conditions. They develop personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific needs.
Treatment options may include prescribing medication to alleviate pain and inflammation, providing wound care for foot ulcers or injuries, performing minor in-office procedures like toenail removal, administering corticosteroid injections for certain conditions, and more.
03 – Foot and Ankle Surgery
Podiatrists are trained to perform surgical procedures when conservative treatments do not yield satisfactory results.
They may conduct foot and ankle surgeries to correct structural abnormalities, address injuries, repair damaged tissues, and improve foot function.
Examples of common podiatric surgical procedures include bunionectomy, hammertoe correction, Achilles tendon repair, ankle arthroscopy, and more.
04 – Orthotics and Footwear
Podiatrists have expertise in prescribing and fitting Orthotic Devices, such as shoe inserts, custom-made orthotics, braces, or splints.
These devices help support the foot’s alignment, provide cushioning, improve stability, and correct biomechanical abnormalities.
Podiatrists also offer guidance on appropriate footwear choices, emphasizing the importance of supportive and well-fitted shoes to prevent and manage Foot Problems.
05 – Foot Care Management
Podiatrists play a crucial role in foot condition ongoing management.
They guide toward self-care practices, including foot hygiene, proper nail trimming techniques, and diabetic foot care for individuals with diabetes.
Podiatrists educate patients on preventive measures, such as exercises to strengthen the feet and ankles, strategies for preventing foot injuries, and steps to minimize the risk of recurring problems.
06 – Specialized Care
Some Podiatrists specialize in specific areas within the field of Foot Health, such as Sports Podiatry, Pediatric Podiatry, Diabetic Foot Care, Geriatric Foot Care, or Foot and Ankle Biomechanics.
These specialized practitioners have in-depth knowledge and experience in managing particular conditions or populations, allowing them to provide focused and comprehensive care.
07 – Collaborative Approach
Podiatrists often work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals, such as orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, primary care physicians, and diabetes specialists, to ensure coordinated and Holistic Care.
They may refer patients to these specialists when necessary or collaborate on multidisciplinary treatment plans to optimize outcomes.
Conclusion
Overall, Podiatrists are highly skilled professionals dedicated to promoting Foot Health, preventing Foot Problems, and addressing a wide array of Foot and Ankle Conditions.
Their expertise, combined with a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management, allows them to provide specialized care to improve patients’ quality of life and overall well-being.
If you’re experiencing foot or ankle issues, consulting a Podiatrist is a wise step toward achieving optimal Foot Health.
V – Home Remedies and Self-Care for Foot Pain and Problems
Your feet are the pedestal of your body (let’s say so), supporting you throughout your daily activities as we’ve said earlier in this post.
And when Foot Pain strikes, it can disrupt your life and hinder your mobility.
This part of the blog post aims to provide you with a treasure trove of Natural Remedies and Self-care Techniques to alleviate Foot Pain and tackle common Foot Problems from the comfort of your own home.
Whether you’re dealing with Bunions or General Foot Discomfort, this resource will empower you with practical tips and techniques to soothe your soles and get you back on your feet (if you have any issues with them).
And you can say hello to happy, healthy feet, thanks to the power of Home Remedies and Self-care Practices.
A – Effective Home Remedies
When it comes to Foot Pain and Problems, finding effective solutions can make all the difference in your daily life.
Luckily, there are numerous Home Remedies that can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
These natural remedies not only provide relief but also empower you to take control of your Foot Health.
Following are some effective Home Remedies for Foot Pain and Problems:
01 – Proper Footwear
Wearing appropriate footwear is essential for Foot Health. Choose shoes that provide adequate support, cushioning, and a proper fit.
Avoid high heels and opt for shoes with arch support and shock absorption to reduce pressure on your feet.
02 – Ice Pack Therapy
Cold therapy is highly effective in reducing pain and inflammation.
Place an ice pack or a bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a thin towel on the affected area for 15 minutes at a time. This can help number the area and provide temporary relief.
03 – Essential Oils Massage
Certain essential oils have soothing and anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate Foot Pain.
Mix a few drops of peppermint, lavender, or eucalyptus essential oil with a carrier oil like coconut or olive oil.
Massage this mixture onto your feet, focusing on the painful areas. The gentle massage combined with the aromatic benefits of the oils can offer relief.
04 – Stretching Exercises
Regular stretching exercises can help relieve Foot Pain and prevent future problems.
Perform simple stretches like calf stretches, toe curls, and ankle rotations to improve flexibility and reduce tension in your feet.
05 – Foot Massage and Acupressure
Massaging your feet stimulates blood circulation, relaxes muscles, and provides relief from pain. You can use your hands, a tennis ball, or a foot roller to massage the soles of your feet.
Additionally, applying gentle pressure on specific acupressure points, such as the ball of your foot or the arch, can help target pain and promote overall well-being.
06 – Warm Compress Technique
For chronic foot pain, a warm compress can work wonders. Dip a washcloth in warm water, wring out the excess, and apply it to the painful area for 10-15 minutes.
The heat helps increase blood flow, relax muscles, and alleviate discomfort.
07 – Epson Salt Soak
Soaking your feet in warm water infused with Epsom salt can work wonders for relieving foot pain. Epsom salt contains magnesium sulfate, which can help reduce inflammation and relax muscles.
Add half a cup of Epsom Salt to a basin of warm water and soak your feet for 15-20 minutes.
Conclusion
Remember, while home remedies can offer relief, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if your foot pain persists or worsens.
They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend additional treatments if necessary.
By incorporating these effective home remedies into your routine, you can take charge of your foot health and find comfort and relief in the comfort of your own home.
B – Exercises for Foot Pain Relief
Exercise can play a crucial role in relieving foot pain and promoting overall foot health.
By targeting specific muscles, improving flexibility, and enhancing circulation, these exercises can help alleviate discomfort and prevent future problems. Here are some effective exercises for foot pain relief:
01 – Toe Stretching
Sit in a chair and extend one leg in front of you. Keeping your heel on the ground, lifting and spreading your toes as wide as possible. Hold this position for a few seconds, then relax.
Repeat this exercise 10-15 times for each foot. Toe stretching helps improve flexibility and strengthens the muscles in your toes, which can alleviate pain caused by conditions like plantar fasciitis and bunions.
02 – Calf Raises
Stand near a wall or sturdy support for balance. Rise onto your tiptoes, and lift your heels as high as you can. Hold this position for a few seconds, then lower your heels back down.
Repeat 10-15 times. Calf raises strengthen your calf muscles and help improve stability, relieving pain associated with conditions like Achilles tendonitis and calf strain.
03 – Arch Roll
Sit on a chair and place a tennis ball or a small massage ball under your foot. Roll the ball back and forth along the length of your arch, applying gentle pressure.
Continue for 1-2 minutes, then switch to the other foot. This exercise helps massage and stretch the plantar fascia, providing relief from conditions like plantar fasciitis and flat feet.
04 – Ankle Alphabet
Sit on a chair and lift one foot off the ground. Imagine drawing the letters of the alphabet with your toes, moving your ankle in a controlled manner.
Complete the entire alphabet, then repeat with the other foot. This exercise helps improve ankle mobility, strengthening the muscles and reducing pain caused by ankle sprains and strains.
05 – Marble Pick-Up
Place a bowl or a towel on the floor and scatter marbles or small objects around it.
Sit on a chair and use your toes to pick up the marbles one by one and place them in the bowl. Repeat this exercise for a few minutes, aiming to pick up as many marbles as possible.
Marble pick-up exercises enhance toe dexterity and strength, helping to relieve pain associated with conditions like Morton’s neuroma and toe arthritis.
06 – Resistance Band Flexion
Sit on the floor with your legs extended in front of you. Loop a resistance band around the ball of your foot and hold the ends with your hands.
Gently flex your foot backward against the resistance of the band, then return to the starting position. Repeat 10-15 times for each foot.
This exercise strengthens the muscles in your feet and improves flexibility, providing relief from various foot conditions.
Conclusion
Remember to start these exercises gradually and listen to your body. If you experience pain or discomfort during any exercise, stop and consult a healthcare professional.
Regularly incorporating these exercises into your routine can help alleviate foot pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall foot health.
C – Heat and Cold Therapy in Foot Pain and Problems’ Cure
Heat and cold therapy are widely recognized as effective methods for managing foot pain and problems.
These therapies, also known as thermotherapy, can help alleviate discomfort, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.
Understanding when to use heat or cold therapy and how to apply them properly can significantly contribute to your foot’s recovery.
Here’s a closer look at the benefits and applications of heat and cold therapy in foot pain and problems:
01 – Heat Therapy
a – Increased Blood Flow
Applying heat to the affected area improves blood circulation, which can accelerate the delivery of oxygen and essential nutrients to the injured tissues.
This increased blood flow helps promote healing and reduces muscle tension.
b – Relaxation and Comfort
Heat therapy has a soothing effect on the muscles and can help relax tight or cramped muscles in the feet. It can also provide a sense of comfort and relief from chronic foot conditions such as arthritis or general foot fatigue.
c – Application Methods
There are several ways to apply heat therapy to your feet. You can use a warm towel, or heating pad, or take a warm foot bath.
Ensure that the temperature is comfortable and avoid excessive heat that may lead to burns or discomfort.
Apply the heat for 15-20 minutes at a time, repeating the process as needed throughout the day.
02 – Cold Therapy
a – Pain and Inflammation Reduction
Cold therapy works by constricting blood vessels and reducing blood flow to the affected area.
This helps reduce inflammation and swelling, and numbs the area, providing relief from acute injuries or conditions such as sprains, strains, or plantar fasciitis.
b – Local Anesthetic Effect
Cold therapy acts as a local anesthetic by numbing the nerve endings, which can temporarily alleviate pain and discomfort.
It is particularly effective during the early stages of an injury or when dealing with acute pain.
c – Application Methods
Cold therapy can be applied using ice packs, ice baths, or frozen gel packs wrapped in a thin cloth. Apply the cold therapy to the affected area for about 10-15 minutes at a time.
To avoid frostbite or skin damage, never apply ice directly to the skin and allow breaks between applications to prevent prolonged exposure to cold.
03 – When to Use Heat or Cold Therapy?
The choice between heat and cold therapy depends on the specific condition and its stage. As a general guideline:
Heat therapy is more suitable for chronic conditions, muscle aches, or stiffness. It is beneficial when there is no active inflammation or swelling.
Cold therapy is typically used for acute injuries, acute pain, or when there is active inflammation or swelling.
It’s important to listen to your body and consult a healthcare professional if you are unsure about the appropriate therapy for your specific condition.
Remember, heat and cold therapy should be used as complementary treatments and not as standalone solutions.
They can be incorporated into a comprehensive treatment plan that includes rest, exercises, and other interventions recommended by your healthcare provider.
By utilizing heat and cold therapy correctly and at the appropriate times, you can effectively manage foot pain, reduce inflammation, and support your foot’s healing process, ultimately facilitating faster recovery and improved foot health.
D – Importance of Rest and Recovery in Handling Foot Pain and Problems
Rest and Recovery play a vital role in effectively managing foot pain and problems. When our feet experience discomfort or injury, it’s crucial to provide them with the rest they need to heal and recover.
Ignoring the importance of rest can prolong recovery time, exacerbate existing issues, and even lead to further foot problems.
Here’s a closer look at why rest and recovery are essential when dealing with foot pain:
01 – Healing Facilitation
Rest allows the body’s natural healing processes to take place.
When you give your feet a break from strenuous activities and excessive stress, it helps reduce inflammation, promotes tissue repair, and allows damaged structures like muscles, tendons, and ligaments to recover.
Healing is a gradual process, and providing adequate rest is crucial to ensure proper recovery.
02 – Further Damage Reduction
Continuing to exert stress on already injured or painful feet can worsen the condition and potentially lead to additional complications.
By resting and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain, you minimize the risk of further damage.
Resting also prevents the development of chronic conditions that may arise from overuse or improper healing.
03 – Inflammation and Pain Reduction
Resting allows inflammation to subsidize, providing relief from pain and discomfort. When you give your feet a break, it helps reduce swelling and eases the strain on affected tissues.
This can significantly alleviate pain caused by conditions such as plantar fasciitis, tendonitis, and stress fractures.
04 – Overuse Injuries Prevention
Overuse injuries occur when you subject your feet to repetitive stress without adequate rest and recovery. Common examples include shin splints, Achilles tendonitis, and metatarsalgia.
By incorporating rest days into your routine, you give your feet a chance to recover and reduce the risk of developing these types of injuries.
05 – Overall Foot Health Maintain
Rest and recovery are not only beneficial when dealing with foot pain but also for maintaining overall foot health.
Regular rest helps prevent fatigue, allows your feet to recover from daily wear and tear, and reduces the likelihood of developing chronic foot conditions.
By prioritizing rest, you can keep your feet in optimal condition for long-term health and mobility.
06 – Complement Treatment Strategies
Rest and recovery should be seen as an integral part of any comprehensive treatment plan for foot pain or problems.
Whether you’re undergoing medical treatment, physical therapy, or home remedies, incorporating adequate rest allows these interventions to work more effectively.
It provides a supportive environment for other treatment modalities to take effect and aids in a faster and more complete recovery.
Conclusion
Remember, rest doesn’t necessarily mean complete inactivity. It involves avoiding activities that exacerbate your foot pain while allowing gentle movements and exercises that promote flexibility and circulation.
It’s important to strike a balance between rest and gentle movements to prevent stiffness and muscle atrophy.
If foot pain persists or worsens despite rest and self-care efforts, it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice.
A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis, recommend specific treatment options, and guide you on the appropriate amount of rest and recovery needed for your specific condition.
By recognizing the importance of rest and recovery, you can actively support your foot’s healing process, prevent further damage, and ultimately regain pain-free mobility and optimal foot health.
VI – Living with Chronic Foot Pain: Tips and Strategies
Dealing with chronic foot pain can be incredibly challenging, impacting various aspects of your daily life.
Regardless of the specific foot condition you’re facing, this section of our blog post is dedicated to providing Valuable Tips and Strategies to help you cope with and manage chronic foot pain effectively.
We recognize the significant physical, emotional, and psychological toll that foot pain can take, and our objective is to empower you with practical advice and insights that can enhance your quality of life.
From Self-care Techniques and Home Remedies, as discussed earlier, to the use of Assistive Devices and Lifestyle Adjustments, we will explore a range of approaches designed to provide relief and improve your overall well-being.
Remember, you don’t have to let foot pain control your life.
Together, let’s navigate these challenges, discover effective solutions, and embark on a journey toward reclaiming comfort, mobility, and a more fulfilling life while living with Chronic Foot Pain.
A – Chronic Foot Pain Coping Mechanism
Living with chronic foot pain can be an ongoing challenge, but there are coping mechanisms that can help you manage your condition and improve your quality of life.
These strategies focus on finding ways to alleviate pain, reduce discomfort, and adapt to your limitations. Here are some effective coping mechanisms for chronic foot pain:
01 – Pain Management Techniques
Explore various pain management techniques to find what works best for you.
This may include using over-the-counter or prescribed pain medications, topical creams or gels, or alternative therapies like acupuncture or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS).
Working with a healthcare professional can help you identify the most suitable pain management options for your specific condition.
02 – Self-Care and Home Remedies
Incorporate self-care practices and home remedies into your daily routine.
This may involve soaking your feet in warm water with Epsom salt, applying ice packs to reduce inflammation, performing gentle foot stretches and exercises, or using foot massage techniques.
These simple yet effective strategies can provide temporary relief and help manage chronic foot pain at home.
03 – Assistive Devices
Consider using assistive devices to support your feet and reduce pain. Orthotic shoe inserts, arch supports, splints, or braces can provide additional cushioning, stability, and alignment.
Custom-made orthotics designed specifically for your feet can offer long-term relief and improved foot function.
04 – Footwear Editing
Wearing appropriate footwear is crucial for managing chronic foot pain. Opt for shoes with ample cushioning, good arch support, and a wide toe box to reduce pressure on sensitive areas.
Avoid high heels or shoes that exacerbate your pain. Additionally, custom-made shoes or shoe modifications, such as lifts or wedges, may be recommended by a podiatrist to address specific foot issues.
05 – Physical Therapy
Engaging in physical therapy can be immensely beneficial for chronic foot pain.
A physical therapist can guide you through exercises and stretches that help improve foot strength, flexibility, and balance.
They can also provide specialized treatments, such as ultrasound or manual therapy, to target specific areas of pain or dysfunction.
06 – Mind-Body Techniques
Explore mind-body techniques like relaxation exercises, meditation, deep breathing, or guided imagery.
These practices can help you manage stress, promote relaxation, and redirect your focus away from the pain.
07 – Emotional Support
Seek emotional support from friends, family, or support groups. Living with chronic foot pain can be emotionally challenging, and having a support network can provide encouragement, understanding, and a space to share your experiences.
Consider joining online communities or local support groups dedicated to chronic pain management.
08 – Lifestyle Adjustments
Make necessary lifestyle adjustments to accommodate your foot pain.
This may include modifying your exercise routine, avoiding high-impact activities, pacing yourself to prevent overexertion, and incorporating periods of rest throughout the day.
Adaptations to your work environment, such as using a standing desk or wearing comfortable shoes, can also alleviate foot pain.
Conclusion
Remember, each person’s experience with chronic foot pain is unique, and it may take time to find the right combination of coping mechanisms that work for you.
Be patient, consult with healthcare professionals, and don’t hesitate to try different strategies until you find what brings you the most relief.
With the right tools and support, it’s possible to effectively cope with chronic foot pain and maintain a fulfilling and active lifestyle.
B – Chronic Foot Pain Lifestyle Adjustments
When living with chronic foot pain, making lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve your day-to-day experience and minimize discomfort.
By implementing certain changes, you can better manage your condition, reduce the aggravation of symptoms, and enhance your overall quality of life.
Here are some lifestyle adjustments to consider for chronic foot pain:
01 – Footwear Selection
Choosing appropriate footwear is paramount in managing chronic foot pain.
Opt for shoes that provide ample cushioning, arch support, and a wide-toe box. Look for brands that offer models designed for specific foot conditions.
Consider custom orthotics or shoe inserts recommended by a podiatrist to provide extra support and alignment.
It’s crucial to avoid high heels, tight shoes, or styles that place excessive pressure on sensitive areas.
02 – Workstation Changes
If your work involves prolonged standing or sitting, make ergonomic adjustments to your workstation.
Use an anti-fatigue mat if standing for extended periods, adjust your chair height to maintain proper posture, and ensure your feet are supported on a comfortable surface.
Consider using a footrest or footstool to reduce pressure on your feet and promote better circulation.
03 – Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular exercise is essential for overall health and can also benefit your foot pain.
Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or using an elliptical machine are gentler on the feet while providing cardiovascular benefits.
Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to design an exercise program that suits your abilities and minimizes stress on your feet.
04 – Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing chronic foot pain. Excess weight places additional strain on your feet and exacerbates symptoms.
By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, you can achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the pressure on your feet and alleviating discomfort.
05 – Pacing and Rest
Listen to your body and practice pacing and rest techniques. Avoid overexertion and take breaks when necessary, especially during activities that exacerbate your foot pain.
Incorporate periods of rest throughout the day, elevating your feet to reduce swelling and giving your feet time to recover.
06 – Assistive Devices
Depending on the severity of your foot pain, assistive devices can provide significant support.
Consider using mobility aids such as crutches, canes, or walkers to reduce weight-bearing on the affected foot.
Orthotic devices, including braces or splints, can provide additional stability and alleviate discomfort during specific activities or at certain times of the day.
07 – Stress Management
Chronic foot pain can take an emotional toll, leading to increased stress and tension.
Incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies that promote relaxation.
Taking care of your mental and emotional well-being can positively impact your experience with chronic foot pain.
08 – Accessibility Changes
Make necessary modifications to your living environment to improve accessibility and reduce strain on your feet.
Install handrails or grab bars in your bathroom, consider a shower chair or a bath seat, and ensure that pathways in your home are clear of obstacles.
These adjustments can enhance safety, reduce the risk of falls, and make daily activities more manageable.
Conclusion
Remember to consult with healthcare professionals, such as podiatrists or physical therapists, who can provide personalized guidance and recommendations based on your specific condition.
By implementing these lifestyle adjustments, you can actively manage chronic foot pain, improve your comfort levels, and maintain an active and fulfilling lifestyle.
C – Chronic Foot Pain Support Resources
Living with chronic foot pain can be challenging, but you don’t have to face it alone.
There are numerous support resources available to help you navigate your journey, find information, connect with others who understand your experiences, and access valuable support.
Here are some support resources for chronic foot pain:
01 – Healthcare Professionals
Establish a strong relationship with healthcare professionals who specialize in foot pain, such as podiatrists, orthopedic surgeons, physiotherapists, or pain management specialists.
These professionals can provide expert guidance, diagnosis, treatment options, and ongoing support tailored to your specific condition.
02 – Support Groups
Joining support groups, whether online or in-person, can be immensely beneficial.
Connecting with individuals who are going through similar challenges can provide a sense of understanding, validation, and a platform to share experiences, tips, and strategies.
You can find online communities, forums, or social media groups dedicated to chronic pain management or foot-related conditions.
03 – Patient Advocacy Organizations
Explore patient advocacy organizations that focus on foot health or chronic pain conditions.
These organizations often provide educational resources, online communities, and support networks for individuals dealing with chronic foot pain.
They may also offer information on the latest research, treatment options, and advocacy efforts.
04 – Educational Websites and Blogs
Access reliable online resources, educational websites, and blogs dedicated to foot health and chronic pain.
These platforms offer valuable information, self-care tips, and insights into managing chronic foot pain.
Stay informed about new treatment approaches, lifestyle adjustments, and emerging research to empower yourself in your journey.
05 – Books and Publications
There are numerous books and publications available that discuss chronic pain management, foot health, and strategies for coping with pain.
These resources can provide you with in-depth knowledge, personal stories, and practical advice.
Look for books written by healthcare professionals, pain specialists, or individuals who have lived through similar experiences.
06 – Pain Management Programs
Inquire about pain management programs offered by healthcare facilities or clinics in your area.
These programs often provide comprehensive treatment approaches that encompass various therapies, education, and support groups.
Participating in a structured pain management program can give you access to a multidisciplinary team of professionals focused on improving your quality of life.
07 – Mental Health Support
Mental Health Support: Don’t neglect the emotional aspect of living with chronic foot pain.
Seeking support from mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, can help you navigate the emotional challenges that come with chronic pain.
They can provide coping strategies, help you develop resilience, and support your overall well-being.
08 – Assistive Devices and Equipment Suppliers
Connect with suppliers or organizations that specialize in assistive devices and equipment for individuals with foot pain or mobility challenges.
These resources can offer guidance on selecting appropriate footwear, orthotic devices, mobility aids, and other assistive technologies that can alleviate discomfort and enhance your daily activities.
Conclusion
Remember, everyone’s journey with chronic foot pain is unique, so finding the right combination of support resources may require some exploration.
Be proactive in seeking the support you need and remain open to trying different avenues.
With the support of healthcare professionals, online communities, educational resources, and assistive tools, you can navigate the challenges of chronic foot pain with greater confidence, knowledge, and resilience.
General Conclusion
This comprehensive guide has shed light on the multifaceted world of Foot Pain and Problems.
We’ve explored the various types of foot pain, their underlying causes, and effective management strategies.
From understanding common foot conditions to learning about preventive measures, suitable footwear, and professional treatments, we have aimed to equip you with valuable knowledge to safeguard your Foot Health.
We emphasized the importance of recognizing symptoms, seeking professional guidance, and adopting proactive approaches to maintain healthy and pain-free feet.
Remember, your feet bear the weight of your entire body, and caring for them is fundamental to your overall well-being.
Whether you’re dealing with occasional discomfort or chronic issues, taking the right steps can significantly improve your quality of life.
By embracing self-care techniques, appropriate footwear, and seeking medical advice when necessary, you can ensure that your feet support you in every step you take.
Thank you for being on this journey to understand and address Foot Pain and Problems. Here’s to healthier, happier, and pain-free feet, empowering you to lead a more active and fulfilling life.
Table of Contents
Share this Post!
Sharing information about managing Foot Pain and Problems can indeed help others who are dealing with these conditions.
Your efforts to spread awareness and knowledge can make a positive impact on many people’s lives.
So, if you found this post helpful and think it can help others, please share it and feel free to do that.
Many people have Foot Pain and Issues, and sharing might make a difference in their lives, even if you don’t know them.
Thank you for your time!